What is Contribution Margin? There goes without saying that knowing your company's profitability is essential when running a business. Many business executives consider their profit margin, which calculates the overall Margin by which sales income surpasses costs.
But it would help to see how a product affects the company's earnings if you looked at the contribution margin.
I spoke with Joe Knight, co-founder and owner of business, author of HBR Tools: Business Valuation, to learn more about how scope of impact functions. Joe Knight claims that "it's a common financial analysis tool that's not very well understood by managers."
What is the contribution margin?
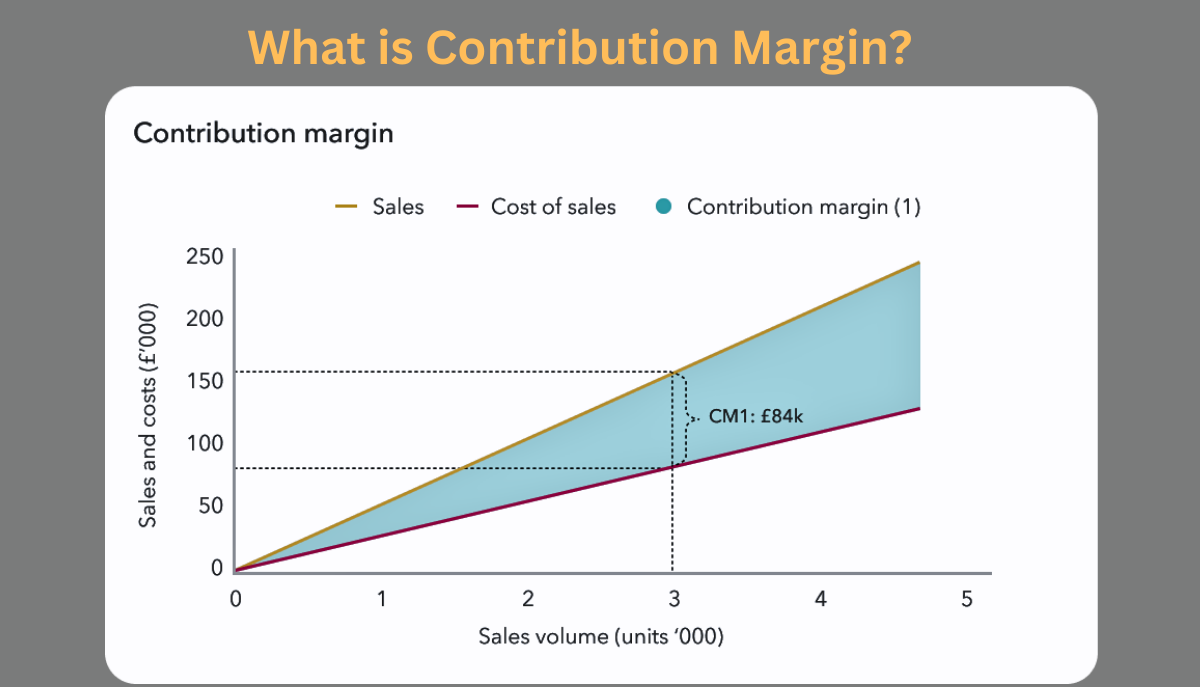
The contribution margin is a financial metric used to measure the profitability of a product or service by calculating the amount of revenue remaining after deducting variable costs.
It provides insights into the portion of sales revenue contributing to covering fixed costs and generating profit. The scope of impact represents the amount available to cover fixed costs and contribute to the bottom line.
Understanding Contribution Margin Calculation
To calculate the scope of impact, you subtract the variable costs associated with producing a product or delivering a service from its corresponding sales revenue.
Variable costs include direct materials, direct labor, and variable overhead. By analyzing the gross margin, businesses can assess the profitability of individual products or services and make informed decisions regarding pricing, production volume, and cost management.
Contribution Margin Calculation Formula
The gross margin is a financial metric representing the remaining revenue after subtracting the variable costs associated with producing or delivering a product or service.
It measures the profitability of individual products or services and provides insight into the company's ability to cover its fixed costs and generate a profit.
The formula for calculating the contribution margin is as follows:
Contribution Margin = Revenue - Variable Costs
To calculate the gross margin, you must determine the revenue generated by a specific product or service and subtract the variable costs directly associated with producing or delivering that product or service.
Here's an example to illustrate the calculation:
Let's say a company sells a product for $50 per unit, and the variable costs per unit, such as raw materials, direct labor, and direct production costs, amount to $30. To calculate the gross margin per unit, you would subtract the variable costs from the revenue:
Contribution Margin per Unit = $50 - $30 = $20
In this case, the gross margin per unit is $20. This means that for every team sold, $20 contributes towards covering the company's fixed costs and generating a profit.
If you want to calculate the gross margin as a percentage, you can use the following formula:
Contribution Margin Ratio = (Contribution Margin / Revenue) * 100
Continuing the previous example, let's assume the company sold 1,000 units. The total revenue would be $50,000 (1,000 units * $50 per unit). To calculate the gross margin ratio, you would divide the contribution margin formula ($20 per unit) by the total revenue ($50,000) and multiply by 100:
Contribution Margin Ratio = ($20 / $50,000) * 100 = 40%
In this case, the gross margin ratio is 40%, indicating that 40% of the revenue generated from the product contributes towards covering fixed costs and generating a profit.
Remember, gross margin analysis is typically used for individual products or services and can provide valuable insights into pricing, cost management, and overall profitability.
Best Examples of Contribution Margin
- Example 1: Real-World Examples: a) A clothing manufacturer sells jeans for $50. The variable costs associated with producing each pair of jeans, such as fabric, labour, and packaging, amount to $30. The contribution margin for each pair of jeans would be $50 - $30 = $20. This means that $20 from each sale contributes towards covering fixed costs and generating profit.
- Example 2: A software company offers a monthly subscription plan for its online service, priced at $100 monthly. The variable costs related to service delivery, including server costs and customer support, amount to $20 per month. In this case, the grmargin for each subscription would be $100 - $20 = $80. This $80 contributes towards covering fixed costs and generating profit.
Leveraging Contribution Margin:
Understanding gross margin enables businesses to make informed pricing strategies, cost control, and resource allocation decisions.
Companies can prioritize and allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on products or services with higher contribution margins. Adjusting pricing strategies based on gross margin analysis can help maximize profitability while remaining competitive.
Ways to Leverage Contribution Margin for Improved Financial Performance:
- Prioritizing Profitable Products or Services: Analyzing gross margin allows businesses to identify and prioritize products or services with higher profitability. By focusing on items with larger contribution margins, companies can allocate resources more efficiently and direct efforts towards areas that generate the most significant financial impact. This strategic approach helps maximize overall profitability and supports effective resource management.
- Guiding Pricing Strategies: Understanding Scope of impact empowers businesses to make informed pricing decisions. By considering a product's or service's gross margin, companies can set prices that ensure optimal profitability while remaining competitive in the market. Accurate pricing based on scope of impact analysis helps maximize revenue and maintain a healthy profit margin.
- Enhancing Cost Control Efforts: Then the Contribution margin analysis assists in effective cost control measures. Businesses can optimize their production processes, negotiate favourable terms with suppliers, and implement cost-saving measures by identifying the variable costs associated with each product or service. Then improving cost efficiency increases the gross margin, allowing for better financial stability and profitability.
- Supporting Strategic Decision Making: Utilizing gross margin as a critical financial metric helps make informed strategic decisions. Whether it's launching new products, discontinuing underperforming ones, or exploring expansion opportunities, gross margin provides valuable insights into the financial viability of different business initiatives. By considering scope of impact in strategic decision-making, companies can mitigate risks and pursue growth opportunities with a clearer understanding of their economic impact.
By leveraging contribution margin, then the businesses can optimize their financial performance, enhance profitability, and achieve long-term success in a competitive business landscape.
Contribution margin uses

A contribution margin is a powerful tool businesses can use to enhance their financial performance. By understanding the uses of gross margin, companies can make informed decisions about pricing, cost control, and resource allocation:
- Gross margin analysis allows businesses to identify and prioritize products or services with higher profitability. By focusing on items with larger contribution margins, because companies can allocate resources more efficiently and direct efforts towards areas that generate the most significant financial impact.
- The scope of impact helps guide pricing strategies. By considering a product's or service's gross margin, businesses can set prices that ensure optimal profitability while remaining competitive in the market.
- Gross margin analysis assists in cost control efforts.
By identifying the variable costs associated with each product or service, then companies can optimize their production processes.
Negotiate favourable terms with suppliers, and implement cost-saving measures to increase the overall scope of impect. By leveraging contribution margin., businesses can drive profitability and achieve long-term financial success.
Importance of Contribution Margin Analysis
Then the Gross margin analysis plays a crucial role in business financial planning and decision-making. It provides valuable insights into the profitability of different products or services and helps identify areas for cost reduction or revenue enhancement.
Companies so, can allocate resources effectively by analyzing the gross margin, optimizing pricing strategies, and making informed decisions on product lines, marketing campaigns, and operational efficiency.
Factors Affecting:
However, some factors can influence the gross margin of a product or service. These include:
- Pricing strategy: Higher prices can increase the scope of impact, so provided the sales volume remains steady.
- Variable costs: Fluctuations in raw materials, labour, or overhead expenses directly impact the gross margin.
- Sales mix: If a company has multiple products or services with varying contribution margins, changes in the sales mix can affect the overall Scope of impact.
- Sales volume: Higher sales can spread fixed costs over a more extensive revenue base, potentially increasing the Gross margin.
Comparing fixed and variable costs
When managing finances and maximizing profitability, businesses must understand the difference between fixed and variable costs.
By grasping the concept of these cost types and their implications, companies can make informed decisions and develop effective strategies to optimize their cost structure.
This article will delve into the definitions of fixed and variable costs, explore examples of each, and highlight their impact on business operations and profitability.
| Fixed Costs | Variable Costs |
| Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production level or sales volume. They are the expenses a business incurs regularly, independent of its output. Fixed costs are usually associated with maintaining the essential operational capacity of a company and are not directly influenced by short-term fluctuations. Specified prices include rent, salaries, insurance premiums, and lease payments. Understanding and effectively managing fixed costs are crucial for long-term financial stability. | In contrast to fixed costs, variable costs fluctuate in direct proportion to the level of production or sales. These costs rise or fall as the volume of output changes. Variable expenses are typically incurred in the production process and are directly tied to the number of units produced or sold. Examples of variable costs include raw materials, direct labor costs, packaging expenses, and commissions. Managing variable costs efficiently is vital for optimizing profit margins and adapting to changes in demand. |
Contribution Margin vs. Gross Margin
While contribution margin focuses on the relationship between sales revenue and variable costs, gross Margin considers the relationship between sales revenue and all costs directly associated with producing a product or service, including variable and fixed costs.
Gross Margin provides a broader picture of profitability, whereas scope of impact explicitly evaluates variable expenses' profitability.
Decision Making
Gross margin analysis is instrumental in various decision-making scenarios, including:
- Pricing decisions: Businesses can determine optimal pricing strategies that maximize profitability by considering the contribution margin.
- Product mix decisions: Companies can evaluate the scope of impact of different products or services to identify those with higher profitability and prioritize their promotion or production.
- Cost management decisions: Gross margin analysis helps identify areas where cost reduction efforts can be focused without adversely affecting profitability.
Limitations
Although contribution margin is a valuable financial metric, it has certain limitations to consider:
- Ignoring fixed costs: The gross margin does not directly account for fixed expenses, essential for long-term sustainability and profitability.
- Oversimplification: By focusing solely on variable costs, the scope of impect overlooks
- Other cost factors that may affect profitability.
- Limited profitability assessment: Scope of impect margin provides insights into product-level profitability but does not assess the overall financial performance of a business.
Real-World Applications of Contribution Margin

Impact of scope analysis finds applications across various industries and business sectors. Some typical real-world applications include:
- Manufacturing companies: gross margin helps assess the profitability of different products or product lines.
- Service-based businesses: Gross margin aids in pricing decisions and evaluating the profitability of various service offerings.
- Retail industry: Scope of impect analysis assists in determining optimal pricing strategies and assessing individual products' profitability.
Benefits of Optimizing Contribution Margin
Optimizing the gross margin offers several benefits for businesses:
- Profitability enhancement: By analyzing and optimizing the gross margin, companies can improve their overall profitability.
- Effective resource allocation: gross margin analysis enables firms to allocate resources efficiently by identifying and prioritizing high-margin products or services.
- Informed decision-making: Then the scope of impact provides insights that help companies to make informed decisions regarding pricing, product mix, and cost management.
Best 5 Effective Strategies to Boost Gross Margin
By implementing the following strategies, you can optimize your scope of impact and achieve sustainable growth for your business.
- Streamline Operational Efficiency: Efficient operations are vital to improving the contribution margin. Conduct a thorough analysis of your business processes to identify areas where efficiency can be enhanced. Look for opportunities to reduce waste, eliminate bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation. By streamlining operations, you can lower variable costs and increase the overall gross margin.
- Implement Cost Control Measures: Controlling costs is essential for improving the contribution margin. Evaluate your expenses meticulously and identify areas where cost reductions can be made without compromising product or service quality. Negotiate with suppliers for better pricing, explore alternative sourcing options, and eliminate unnecessary expenses. By effectively managing costs, you can boost your scope of impact significantly.
- Enhance Pricing Strategies: Pricing is critical in determining the scope of impact. Analyze your pricing structure to ensure it aligns with market demand and accurately reflects the value of your products or services. Conduct market research to understand customer preferences, competitor pricing, and perceived value. Adjust your pricing strategy accordingly to maximize revenue and improve the contribution margin.
- Focus on High-Margin Products or Services: Identify your high-margin products or services and prioritize their promotion and sales. By focusing on these offerings, you can capitalize on higher profit margins and increase the overall scope of impact Allocate resources strategically to boost your high-margin products' sales and marketing efforts while maintaining a diverse product portfolio to cater to different customer segments.
- Invest in Employee Training and Development: Well-trained employees can contribute significantly to improving the scope of impact Invest in training programs that enhance employees' skills and knowledge, enabling them to perform their roles more efficiently. Practical training can increase productivity, reduce errors, and improve customer satisfaction, ultimately positively impacting the gross margin.
How Companies Utilize Contribution Margin to Drive Profitability?
Companies utilize the contribution margin as a vital financial metric to assess profitability and make informed business decisions. Then the scope of impact represents the amount of revenue remaining after subtracting variable costs directly associated with production or service delivery.
By analyzing this metric, businesses gain insights into the profitability of specific products, services, or business segments.
This information helps companies determine because which offerings contribute the most to their bottom line and guides resource allocation and strategic planning.
Additionally, the contribution margin aids in setting optimal pricing strategies, identifying cost-reduction opportunities, and evaluating the organization's overall financial health. By leveraging the scope of impact, companies can make data-driven decisions to maximize profitability and drive sustainable growth.
What Errors Do People Commit?
Understanding these mistakes so, can help individuals and businesses avoid them and make more informed decisions. Some of the critical errors related to contribution margin include:
1. Neglecting Fixed Costs: The scope of impact focuses on variable costs, but it's essential not to overlook fixed costs. While scope of impact helps determine the profitability of individual products or services, fixed costs still need to be covered to ensure overall profitability. Ignoring fixed costs can lead to inaccurate assessments of profitability and potential losses.
2. Inaccurate Allocation of Costs: Assigning costs incorrectly can distort the gross margin analysis. It's crucial to accurately allocate costs to specific products or services to calculate the scope of impact. Please do so to avoid misinterpretation of profitability and incorrect decision-making.
3. Insufficient Data Analysis: gross margin analysis requires a comprehensive evaluation of costs and revenues. Gathering and analyzing sufficient data to ensure complete and accurate insights is critical. Then collecting reliable and detailed information is essential for a more precise scope of impact calculation.
4. Neglecting Market Dynamics: Contribution margin analysis should consider market dynamics, including customer preferences, competition, and industry trends. So, it is essential to consider these factors to avoid inappropriate pricing decisions and product/service strategies. Understanding the market environment is crucial for maximizing scope of impact.
5. Lack of Regular Review: Contribution margin analysis should be an ongoing process rather than a one-time assessment. Failing to review and update scope of impact calculations regularly can result in outdated and ineffective decisions. Periodically monitoring and reassessing contribution margins helps identify changes in costs, revenues, and market conditions, enabling timely adjustments.
6. Overlooking Revenue Potential: Contribution margin analysis primarily focuses on costs, but revenue potential should be addressed. Maximizing scope of impact involves not only cost control but also revenue optimization. Ignoring opportunities for revenue growth can limit the potential for higher contribution margins and overall profitability.
7. Failure to Consider Long-Term Implications: Contribution margin analysis should consider the long-term implications of decisions. A short-sighted approach that prioritizes immediate profitability without considering the future can lead to missed opportunities or negative consequences in the long run. It's essential to consider the sustainability and growth potential of the business when analyzing the gross margin.
By being aware of these common mistakes, individuals and businesses can improve their scope of impact analysis, make more accurate decisions, and enhance overall profitability.
Conclusion
The contribution margin is a vital financial metric that enables businesses to evaluate the profitability of their products or services.
Companies can make informed decisions to optimize pricing, enhance profitability, and effectively allocate resources by analyzing the scope of impact.
However, it is essential to consider the limitations of the scope of impact and use it in conjunction with other financial metrics for a comprehensive assessment of business performance.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How is the contribution margin different from net profit?
The gross margin represents the portion of sales revenue covering fixed costs, whereas net profit is the remaining amount after deducting all expenses, including fixed and variable costs.
Can the contribution margin be negative?
The scope of impact can be harmful if the variable costs exceed the sales revenue. This indicates that the product or service needs to generate more revenue to cover its variable costs.
Is the contribution margin the same as the operating profit?
No, contribution margin and operating profit are not the same. Operating profit considers variable and fixed costs, while scope of impact only focuses on varying costs.
Q4: How can businesses improve their contribution margin?
Businesses can improve their gross margin by optimizing pricing strategies, reducing variable costs, increasing sales volume, and focusing on high scope of impact products or services.
Is the contribution margin applicable only to manufacturing businesses?
No, gross margin analysis applies to various industries, then including manufacturing, services, and retail, where it helps evaluate profitability and make informed decisions.